Key Takeaways
- Ghost chains are blockchains that remain technically operational but have little to no genuine usage, development, or community participation.
- Warning Signs are low transaction volume, inactive communities, stalled developer activity, outdated websites, and exchange delistings.
- Even well-funded or corporate-backed projects like Diem, KodakCoin, and Luna have collapsed when adoption stalled.
- To avoid ghost chains, monitor onchain metrics, developer commits, token liquidity, and community health before investing time or money.
Introduction
The blockchain industry is filled with groundbreaking innovations, multi-billion-dollar ecosystems, and promises of decentralizing the internet. Yet, hidden among the headlines and hype lies an uncomfortable reality — many blockchain projects quietly fade into obscurity. These forgotten networks, known as ghost chains, continue to run in a technical sense but lack real-world utility, active development, or an engaged community.
For investors, developers, and enthusiasts, recognizing the early signs of a ghost chain is essential to avoiding costly mistakes. In this guide, we’ll explore what ghost chains are, how to identify them, famous examples of their downfall, and the risks they pose to the wider crypto ecosystem.
Ghost Chain Explained
A ghost chain is a blockchain network that still functions on a technical level but has been effectively abandoned by its developers and community. While some ghost chains once enjoyed momentum and heavy promotion, they eventually experience:
- Stalled development — no significant code updates for months.
- Falling engagement — user activity and transaction volume drop sharply.
- Diminished utility — the network no longer serves a compelling purpose.
The blockchain may still process blocks and transactions, giving the illusion of life, but beneath the surface, it’s effectively dead. This gradual decline can occur for various reasons: loss of funding, overhyped but underdelivered promises, competition from more active projects, or simple community disinterest.
From once-promising Ethereum killers to obscure layer-1 networks, the blockchain graveyard is littered with examples of projects that couldn’t sustain growth. Recognizing the signs early can mean the difference between a smart investment and becoming trapped in a digital ghost town.
Common Traits of a Ghost Chain
While not every slowing blockchain qualifies as a ghost chain, these recurring indicators are strong red flags:
- Diminished Developer Activity
- Few or no recent code commits, version updates, or bug fixes.
- Public GitHub repositories may remain untouched for months.
- Inactive Communities
- Forums, Telegram groups, and Discord channels show little or no discussion.
- Official social accounts (e.g., X/Twitter) may go months without updates.
- Broken or Outdated Websites
- Stale project information, outdated roadmaps, or missing documentation.
- Low Onchain Transaction Volume
- Only a handful of transactions per day, often automated or from bots.
- Exchange Delistings & Low Trading Volume
- Native tokens delisted from major exchanges or trading with extremely thin liquidity.
These factors often combine, leaving the network technically alive but commercially irrelevant.
How to Investigate and Identify Ghost Chains
Avoiding ghost chains requires careful research before committing time, funds, or development resources.

1. Examine Transaction Data
- Use blockchain explorers to verify block production and transaction frequency.
- Some ghost chains process fewer than 10 transactions per day, often with nearly empty blocks.
2. Check DApp Activity
- A thriving chain should have decentralized apps, DeFi platforms, NFT marketplaces, and active smart contracts.
- An empty ecosystem signals low adoption and developer disinterest.
3. Assess GitHub or Repository Updates
- Look for recent commits, bug fixes, and feature rollouts.
- If the last meaningful update was 6+ months ago, proceed with caution.
4. Monitor Social Media & Community Channels
- Healthy chains host regular AMAs, dev updates, and user discussions.
- Empty Telegram chats, bot-filled Discord servers, or inactive Twitter feeds are bad signs.
5. Review Token Performance
- A consistently falling token price with minimal trade volume suggests abandonment.
- While price alone doesn’t prove failure, it often mirrors community and developer disengagement.
6. Look for Event Participation
- Check if the project team attends crypto conferences, hosts meetups, or participates in industry panels.
- A total absence from events is often a sign of slow decline.
Pro Tip: watch for extravagant marketing claims such as “100,000 TPS”, “Ethereum killer”, or “fastest chain in the world”. Without delivery, these slogans often precede ghost chain status.
Ghost Chain Examples
The crypto industry has no shortage of ghost chain casualties. Some notable cases include:
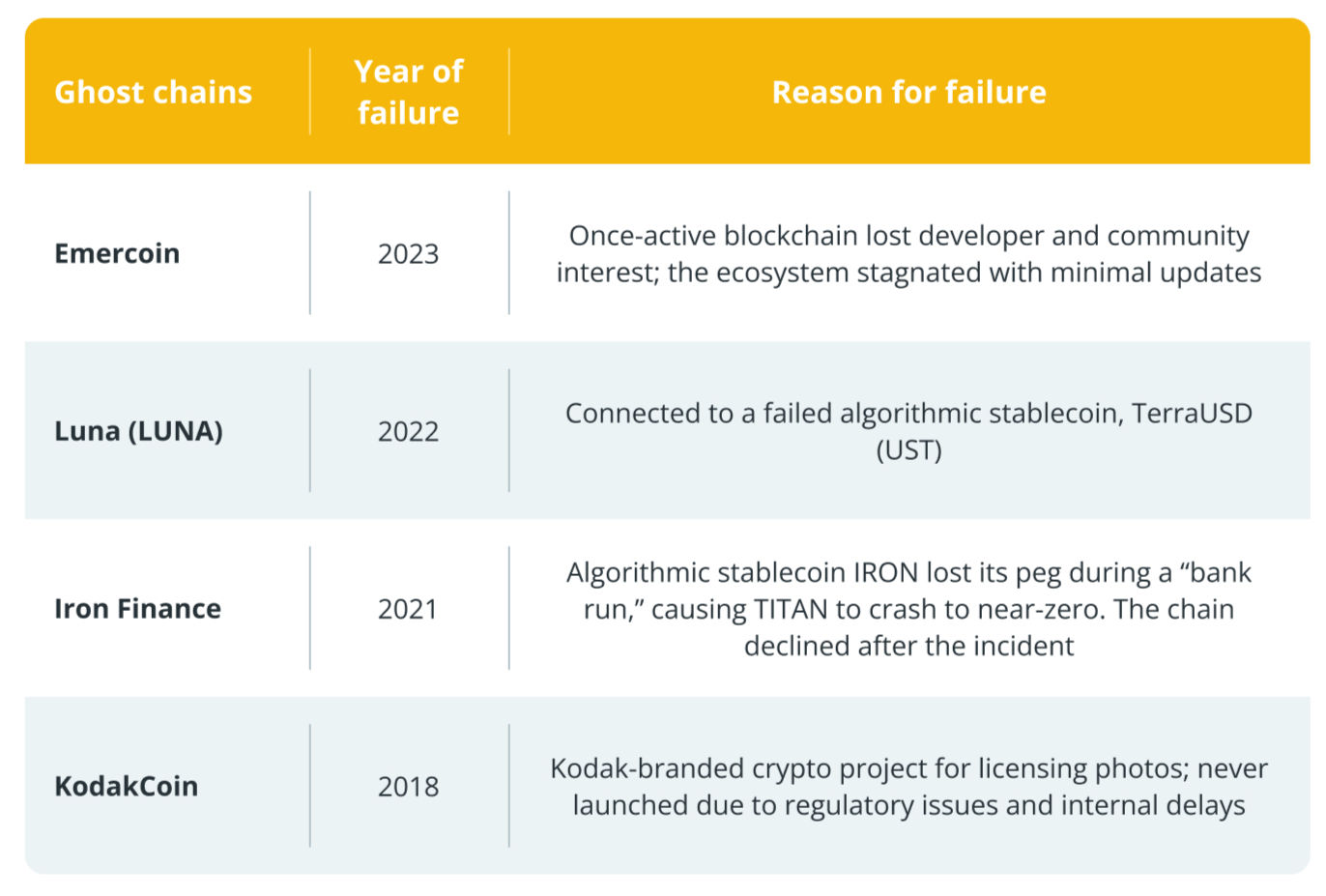
While each failed for unique reasons, the common thread is the inability to maintain an active, engaged ecosystem.
Risks and Consequences of Ghost Chains
Ghost chains carry significant risks, both financial and security-related:
- Loss of Investor Capital — Tokens lose value as liquidity dries up.
- Wasted Development Effort — Time and resources spent on a dying platform.
- Erosion of Trust — Failures damage confidence in blockchain as a whole.
- Security Threats — Abandoned domains, old wallets, and unmaintained smart contracts can be exploited by scammers.
Some inactive chains do see revivals — often through rebranding, community takeovers, or new funding — but such comebacks are rare exceptions.
Conclusion
In the fast-paced world of blockchain, hype can propel projects to meteoric heights — but without sustained development, user adoption, and utility, even the most promising chains risk becoming ghost chains. For investors and developers, learning to spot these signs early is one of the most valuable survival skills in the crypto space. By staying vigilant, analyzing onchain activity, and assessing community health, you can avoid wasting resources on networks destined for the blockchain graveyard.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are all low-activity blockchains ghost chains?
No. Some blockchains intentionally serve niche purposes with low transaction volume but remain functional and maintained.
Can ghost chains be revived?
Yes, though rarely. Revival often requires significant new investment, a fresh development team, or a strong community push.
How quickly can a blockchain become a ghost chain?
It can happen in under a year if funding dries up, adoption stalls, or critical development halts.
What’s the best way to check if a project is still alive?
Monitor GitHub activity, transaction counts, social media updates, and whether the team is attending industry events.
Why do well-funded projects like Luna still fail?
Funding can’t compensate for flawed tokenomics, poor risk management, or loss of community trust.
