Introduction
Clicking a phishing link can hand cybercriminals the keys to your financial life, professional network or personal identity. Sometimes it happens in an instant. The culprit might be an urgent email from your bank or a message that appears to come from your workplace. Scammers strike when your guard is down. One click, and you realize your action has put you at serious risk. The minutes following an accidental click are extremely important. Your reaction can make the difference between a minor scare and a financial or data disaster. Instead of panicking, take quick action to contain the threat. This article provides a five-step action plan to immediately limit unauthorized access and help you regain control. These are fast, definitive measures designed to prevent disaster.
Key Takeaways
- The most critical action after clicking a phishing link is to disconnect from the internet immediately to prevent malware from communicating with external servers or spreading further through your network.
- Changing your passwords using a safe, uncompromised device and enabling two-factor authentication across all sensitive accounts can significantly reduce unauthorized access risks.
- Running a comprehensive antivirus and anti-malware scan on your device helps detect and remove malicious files while updating your operating system patches known vulnerabilities.
- Monitoring all your accounts for suspicious activity, enabling real-time alerts, and contacting your financial institutions if you notice anything unusual are essential steps to minimize potential damage.
- Reporting the phishing attempt to official agencies and learning from the experience by implementing stronger cybersecurity practices, such as using password managers and anti-phishing browser extensions, helps protect you from future attacks.
Immediate Action: Disconnect From The Internet Immediately
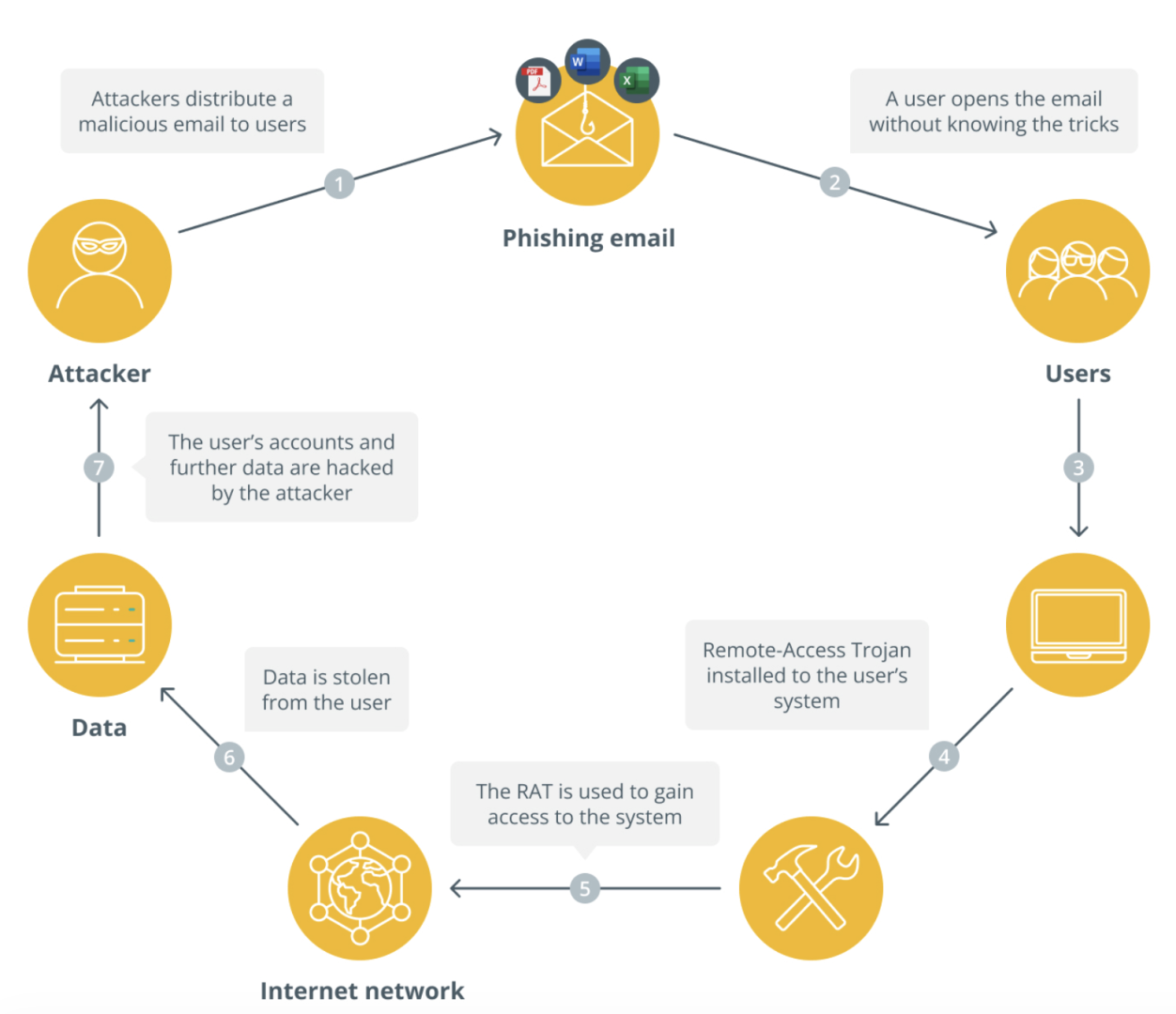
When you realize you have clicked a phishing link, the first and most critical action is to disconnect from the internet immediately. Turn off your WiFi or mobile data to prevent malware from communicating with external servers or spreading further. This simple action stops any potential infection from advancing and limits the attacker’s ability to access your system remotely. Avoid any further browsing or interaction with the suspicious page, as continued clicking could trigger additional security risks or cause further malware installation.
If you are using a work device, notify your IT department promptly so they can isolate the system, secure evidence and begin a comprehensive security assessment. Acting quickly in a workplace environment is crucial to protect your company’s data, block unauthorized access and stop malware from spreading through your organizational network. Time is absolutely critical when responding to phishing incidents, as every minute counts in preventing broader system compromise.
Protecting Your Accounts: Change Compromised Passwords Immediately
After addressing the initial threat by disconnecting from the internet, your next priority is changing your passwords. Start by identifying which accounts may be at risk, especially those linked to email, banking, social media or cryptocurrency wallets that were connected to the affected device or phishing link. Use a secure, unaffected device to reset these passwords and make sure each one is strong and unique. Generate passwords that are at least 16 characters long and include a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers and special characters.
Whenever possible, enable two-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security beyond your password. This approach requires a second verification step, such as a code from your authenticator app or a one-time SMS message, which prevents unauthorized access even if your credentials were compromised. Acting quickly to update passwords reduces the attacker’s opportunity to exploit your accounts and helps you regain control of your digital identity.
Strong Password Requirements After A Phishing Click
Creating strong passwords is your first line of defense against unauthorized account access. Your new passwords should be unique for each account, contain at least 16 characters and include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and special characters. Avoid using personal information such as birthdates, names or common words that attackers can easily guess through social engineering or dictionary attacks.
Two-Factor Authentication Setup For Enhanced Protection
Two-factor authentication provides a second barrier that significantly increases account security. Most email providers, banks and cryptocurrency exchanges now support multiple 2FA methods, including authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or Authy, which are generally more secure than SMS-based authentication. Physical security keys offer the highest level of protection and should be considered for your most sensitive accounts. Setting up 2FA across all accounts that support it should be one of your immediate priorities.
Cryptocurrency Wallet And Exchange Account Security
If the phishing link targeted any accounts connected to cryptocurrency wallets or exchanges, extra caution is required. Change the password immediately and enable all available security features, including withdrawal whitelisting, API key restrictions and two-factor authentication. If you suspect any unauthorized transactions or transfers occurred, contact your exchange’s support team immediately and request they freeze your account while investigating potential unauthorized activity.
Device Security: Run A Full Antivirus And Anti-Malware Scan
After securing your accounts, inspect your device for potential threats by running trusted antivirus or anti-malware software. These programs detect and remove any malicious files that may have been downloaded through the phishing link, protecting your system from further compromise. On mobile devices, clear the cache thoroughly, delete any suspicious apps that you did not intentionally install and review app permissions for any unauthorized changes that malware may have made.
Once your device is clean, update the operating system and browser to patch known vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit. Running a thorough scan not only removes existing threats but also strengthens your device’s overall security posture. Make sure that no malware remains on your device because it could jeopardize your data or accounts in the future. Schedule regular scans on a weekly or bi-weekly basis as part of your ongoing security maintenance routine.
Choosing The Right Antivirus Software For Your System
Selecting reputable antivirus software is essential for effective threat detection and removal. Look for solutions that offer real-time protection, automatic updates and regular malware definition updates. Avoid free or unknown antivirus programs, as they may be unreliable or contain malware themselves. Well-established options such as Kaspersky, Norton, McAfee and Bitdefender offer comprehensive protection against various threats.
Browser And Operating System Security Updates
Updating your browser and operating system as soon as patches become available closes security vulnerabilities that attackers exploit. Enable automatic updates whenever possible so you do not miss critical security patches. Review your browser extensions and plugins, as older or abandoned extensions can become security risks. Remove any extensions you no longer use or do not recognize.
Ongoing Device Maintenance And Regular Scanning Schedule
Creating a regular maintenance schedule helps prevent future infections. Set reminders to scan your device weekly or bi-weekly with your antivirus software. Update all installed applications regularly, as outdated software often contains known vulnerabilities. Monitor your device’s performance for signs of infection, such as unusual slowness, unexpected pop-ups or strange network activity.
Account Monitoring: Stay Alert For Suspicious Activity
Even after securing your device, stay alert and monitor all your online accounts for signs of unauthorized activity. Watch for unfamiliar logins from new locations or devices, unexpected transactions or unusual messages from your bank, email provider or cryptocurrency exchange. Cybercriminals may act immediately after obtaining your information or wait weeks or months before exploiting stolen credentials. If you notice anything suspicious, contact your bank, email provider or cryptocurrency exchange immediately to freeze accounts or reverse any unauthorized transactions.
To stay proactive, enable real-time alerts for account changes, password resets or withdrawals. Most major financial institutions and email providers allow you to set up notifications whenever sensitive account activity occurs. Consistent monitoring helps you respond quickly if hackers gain access, reducing potential damage to your financial or digital accounts. Some services also offer fraud monitoring that automatically alerts you to suspicious patterns or transactions.
Setting Up Real-Time Account Alerts And Notifications
Real-time alerts provide immediate notification when suspicious activity occurs on your accounts. Configure your bank to send alerts for any transaction above a certain threshold, password changes, or login attempts from unrecognized locations. Email providers typically offer alerts for new device logins and password changes. Cryptocurrency exchanges usually provide alerts for withdrawals, API key changes and account modifications.
Recognizing Signs Of Unauthorized Access On Your Accounts
Learn to identify the warning signs of compromised accounts to catch attacks early. These signs include unauthorized transactions, unexpected password reset emails, unknown login attempts from unfamiliar locations or devices, and sudden changes to your account settings or recovery information. Act immediately if you notice any of these indicators.
Working With Your Bank And Financial Institution
If you notice unauthorized transactions, contact your bank immediately. Most banks offer fraud protection that may reverse unauthorized transactions within a certain timeframe. Provide them with detailed information about what occurred and when. Your bank can place a fraud alert on your account and monitor for further suspicious activity.
Reporting And Recovery: Take Action With Official Authorities
After securing your devices and accounts, the final step is to report the phishing attempt to the appropriate authorities. If you are in the United States, forward the email or message to the Internet Crime Complaint Center. In the United Kingdom, report phishing to Action Fraud, and in Scotland, to Police Scotland. In India, file your complaint with the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team. You can also share the suspicious link with Google Safe Browsing to help block similar threats to other users.
If you accessed the link using a work account, promptly notify your IT support team so they can take appropriate action within your organization. If your country does not have a dedicated online reporting system, file a report with your local police. These reports help law enforcement agencies track phishing campaigns and identify the criminals behind them. Your report also becomes part of a larger database that helps protect others from the same scams.
Reporting To Government And Official Agencies
Official reporting channels exist in most countries to help track and combat phishing attacks. The Internet Crime Complaint Center accepts reports from the United States and processes them for law enforcement investigation. Action Fraud in the United Kingdom handles fraud and phishing reports from across the country. Police Scotland manages reports from Scotland specifically. The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team coordinates cyber incident responses across India.
Notifying Your Email And Service Providers
Contact your email provider and all other affected service providers directly about the phishing attempt. They can investigate the suspicious email, mark it as phishing and use this information to improve their security systems. Reporting phishing attempts through your email provider’s built-in reporting tools sends valuable data that helps them identify phishing campaigns earlier and protect other users.
Using Google Safe Browsing To Block Similar Threats
Google Safe Browsing allows you to report phishing links and malware URLs directly. Submit the suspicious URL through their reporting tool so that Google can investigate and potentially block the link from appearing in search results or browser warnings. This action helps protect millions of other Google users from the same threat.
Learning From The Experience: Strengthen Your Long-Term Security
While clicking a phishing link can be alarming, it can also be a valuable learning experience if you take the right lessons from it. In the face of adversity, stay composed, respond promptly and treat the incident as an opportunity to improve your cybersecurity practices. Once you have addressed the immediate threat, focus on safeguarding your accounts and devices through stronger security measures and better awareness.
Strengthen your online security by using a reputable password manager that generates and stores strong, unique passwords for all your accounts. Install anti-phishing browser extensions that warn you before you visit suspicious sites. Keep your security software up to date and ensure that automatic updates are enabled on all your devices. To stay protected in the future, stay informed about new developments in cybersecurity and evolving phishing tactics. Even experienced users can make mistakes, so continuous learning and awareness are essential. Making cybersecurity a regular habit and staying vigilant will keep you protected against future attacks.
Password Managers For Secure Credential Management
Password managers eliminate the need to remember multiple complex passwords by securely storing them in an encrypted vault. Popular options such as Bitwarden, 1Password and LastPass make it easier to use unique passwords for every account. Password managers also help identify weak passwords that need updating and can automatically change passwords if you configure them to do so.
Anti-Phishing Browser Extensions And Tools
Browser extensions specifically designed to detect phishing attacks provide an additional layer of protection. These tools analyze websites you visit and warn you if they match known phishing patterns. Popular anti-phishing extensions include PhishProtection, Netcraft and Avast Online Security. These extensions work continuously in the background to protect you without requiring any active effort.
Conclusion
Staying informed about cybersecurity threats helps you recognize and avoid phishing attempts. Follow cybersecurity news sources, take online courses about phishing and social engineering tactics, and participate in security awareness training when offered by your employer. Understanding how attackers think and operate helps you recognize suspicious messages and links before clicking them.
Fast Facts
- Phishing attacks cost organizations over $3.8 billion annually in losses, according to the Anti-Phishing Working Group, making rapid response to a phishing click absolutely critical to preventing financial loss.
- Changing your passwords within 15 minutes of clicking a phishing link significantly reduces the likelihood that attackers can use stolen credentials to access your accounts before the password change takes effect.
- Two-factor authentication blocks 99.9 percent of automated cyberattacks, according to Microsoft research, making it one of the most effective security measures you can implement immediately after a phishing incident.
- Malware installed through phishing links can remain dormant in your system for weeks or months before activating, which is why running periodic antivirus scans and maintaining updated security software is essential even after the initial incident.
- Over 90 percent of data breaches are initiated through phishing or social engineering tactics according to Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report, highlighting why learning from your experience and improving your awareness is crucial for long-term security.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if I clicked a phishing link but did not enter any information?
Even if you did not enter any sensitive information, clicking a phishing link can still pose risks. The link may download malware to your device, which could remain dormant until the attacker decides to activate it. Disconnect from the internet immediately, run antivirus scans to remove any potential malware and monitor your accounts for suspicious activity. Your vigilance in taking these steps will minimize any potential damage even when no credentials were entered.
How long should I monitor my accounts for suspicious activity after clicking a phishing link?
Cybercriminals may use stolen information immediately or wait weeks, months or even longer before exploiting compromised accounts. Continue monitoring for at least three to six months after the incident, though maintaining indefinite vigilance is the safest approach. Setting up permanent alerts and regularly reviewing account activity helps protect you long-term. If you notice anything suspicious even years later, take immediate action.
Can my device be hacked just from clicking a phishing link without downloading anything?
Some phishing links lead to malicious websites that exploit browser vulnerabilities to automatically download and install malware without your knowledge or permission. Other links simply attempt to capture your information if you enter it on a fake login page. Running a comprehensive antivirus scan will detect any hidden malware installations. Disconnecting from the internet immediately after clicking a phishing link reduces the likelihood that a drive-by download attack succeeds.
Should I change passwords on my other devices if I clicked a phishing link on one device?
If the phishing link was accessed from a single device and that device was the only one used to access the compromised accounts, you can change passwords using another device first. However, if you have logged into any of the affected accounts from other devices, those devices could also be at risk. For maximum security, change passwords from a clean device that was not exposed to the phishing link and consider running security scans on all devices you regularly use for account access.
What should I do if I entered my password on a phishing website?
If you entered your password on a phishing site, change it immediately using a different, secure device that was not exposed to the phishing link. Once you have changed your password, the old password becomes useless to attackers, though they will know your account exists. Monitor that account very closely for unauthorized access and enable two-factor authentication if it is not already active. If the phishing website also captured other personal information, consider placing a fraud alert with credit reporting agencies as a precautionary measure.
