Key Takeaways
- zkSync uses zero-knowledge proofs to improve Ethereum’s scalability, security, and cost efficiency.
- Developed by Matter Labs, zkSync 2.0 offers major improvements over version 1.0, including zkEVM compatibility.
- zk-Porter boosts potential throughput from 3,000 TPS to 20,000 TPS.
- zkSync’s fees are about 50 times cheaper than Ethereum’s mainnet (RMB 1.5 vs. RMB 75).
- More than 100 DApps already operate on zkSync, signaling strong ecosystem growth.
- A zkSync token and airdrop are expected, potentially rewarding early adopters.
Introduction
The Ethereum blockchain, driven by the massive rise of decentralized finance (DeFi), smart contracts, and the growing adoption of nonfungible tokens (NFTs), has drawn enormous global attention. Despite its innovation and value, DeFi and NFT activities require substantial energy and come with high transaction costs. Ethereum’s reliance on the proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism, once popular, has now become one of its main challenges, especially when combined with elevated gas fees.
To address issues related to scalability and costly transactions, Ethereum’s developers created a new consensus layer to improve efficiency. This evolution led to the introduction of advanced solutions such as zero-knowledge rollups, zkSync, and Optimistic Rollups.
ZkSync, in particular, allows users to move in and out of the Ethereum mainnet in a decentralized and efficient manner while significantly reducing transaction fees compared to
Ethereum’s legacy model. The advantages of zero-knowledge proofs (zkProofs) include faster processing and lower gas fees, which solve two major pain points for Ethereum users.
This guide explores zk-Rollup technology, the origins of zkSync, how zkSync compares with other layer-2 (L2) solutions, zkSync’s token prospects, its advantages, decentralized applications (DApps) operating on zkSync, and the zkSync bridge.
What is zkSync?
ZkSync is an advanced scaling solution that implements zero-knowledge (zk) rollups to enhance Ethereum’s performance. The term “zk” stands for zero knowledge, while “rollups” refer to smart contracts that aggregate multiple transactions off the main Ethereum layer and then combine them into a single transaction.

Zero-knowledge proofs, or zk-Proofs, rely on cryptographic validation that confirms the accuracy of a transaction without exposing any private details. This innovation ensures integrity, efficiency, and privacy within the zkSync ecosystem.
zkSync vs. Other Layer-2 Solutions
Layer-2 networks such as Polygon, Optimism, Arbitrum, and Immutable X were developed to improve Ethereum’s scalability and performance. Each provides unique approaches to solving problems related to throughput, gas costs, and functionality, though none is a perfect solution. Rollups, however, attempt to strengthen all these aspects simultaneously.
Layer-2 Rollups
A zk-Rollup is a layer-2 scalability method that processes multiple transactions off-chain and then records them as a single transaction on Ethereum, enabling faster and cheaper validation.
Optimistic Rollups also enhance scalability but differ in their approach. Instead of performing computations immediately, they assume transactions are valid by default and only verify them if a challenge occurs. This reduces network congestion and minimizes gas expenses.
Zk-Rollups, by contrast, use cryptographic validity proofs to instantly confirm transaction accuracy. While this makes them more secure and efficient, it also increases technical complexity, particularly in developing zk-Rollups that are fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
zkSync-Compatible Bridges
A blockchain bridge connects two networks by synchronizing token supply through minting and burning processes, allowing smooth asset transfers. Developers appreciate these bridges because they speed up operations and improve interoperability.
Notable zkSync bridges include:
- zkSync Portal: A trustless protocol that integrates zero-knowledge proofs to enable fast, low-cost transactions on Ethereum. All assets are held in a single smart contract on the main chain, while data computation happens off-chain.
- ZigZag Bridge: Part of the ZigZag decentralized exchange (DEX), this bridge allows users to transfer funds seamlessly between networks. It also provides an accessible interface where users can review transfer histories.
Who is Behind zkSync?
ZkSync was developed by Matter Labs, a Germany-based company that began working on zero-knowledge Rollups in 2019 to improve Ethereum scalability. The first version, zkSync 1.0, launched in 2020.
- zkSync 1.0: Introduced in 2020, it was capable of processing up to 3,000 transactions per second (TPS). However, as network demand grew, Matter Labs saw the need for a more powerful version.
- zkSync 2.0: The new release introduced a zkEVM testnet, making zkSync the first zk-Rollup to execute Ethereum-native smart contracts. With its alpha zkEVM infrastructure, zkSync 2.0 represents a significant upgrade from version 1.0.
Matter Labs also developed zk-Porter, a sharding-based scalability feature that boosts efficiency. With zk-Porter, throughput could increase from 3,000 TPS to as high as 20,000 TPS, demonstrating the enormous potential of zkSync technology.
zkSync Token
Currently, zkSync does not have its own native token. However, Matter Labs has indicated that a token launch may occur in the future to allow investors to stake and participate as zkSync network validators.
The team has also hinted at a zkSync airdrop, potentially similar to Optimism’s token distribution. Updates from zkSync’s official tokenomics page suggest that loyal network users could benefit once the token becomes available.
How the zkSync Ecosystem Works
Zk-Rollups scale Ethereum by executing transactions off the main Ethereum chain (layer 1) while still submitting transaction data to layer 1 for security. This approach maintains the security and decentralization of Ethereum but at a fraction of the cost.
The zkSync model thus improves throughput, reduces fees, and preserves the integrity of the main blockchain’s structure.
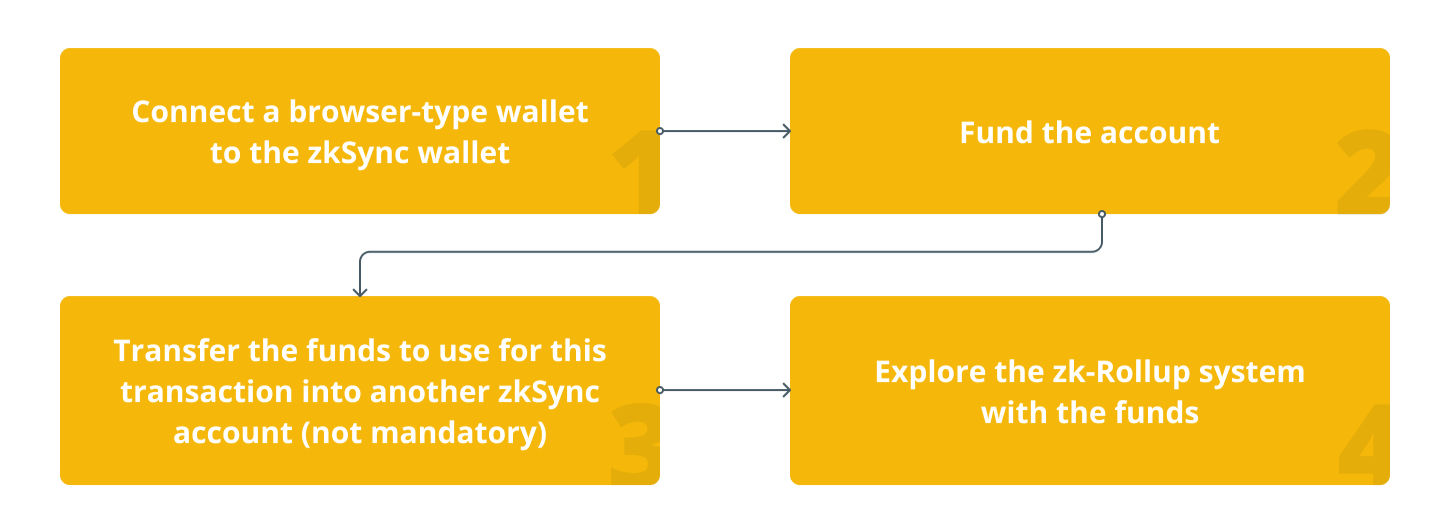
Steps to Start Using zkSync
Pros and Cons of zkSync
Pros
- Flexible fee payments: Users can pay fees in various supported tokens rather than strictly in Ethereum. For example, if transferring a stablecoin like Tether, users can pay the fee with Tether itself.
- Faster transactions: Withdrawal times are shorter, often around three hours for funds to reach the recipient’s account.
- Lower costs: The difference in transaction fees is substantial. While a token transfer on Ethereum’s mainnet costs about RMB 75, the same transfer on zkSync costs roughly RMB 1.5.
Cons
- Centralization risks: Some consensus mechanisms, such as practical Byzantine fault tolerance (pBFT) and delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS), enhance speed but may reduce decentralization.
- Exchange compatibility issues: Not all wallets and exchanges are synchronized with layer-2 networks, creating risks of lost transactions if tokens are sent incorrectly.
- EVM support challenges: Full EVM compatibility is still developing. The complexities of proof generation can slow processing and introduce reliability issues.
DApps on zkSync
According to Zk_Daily, an educational Twitter account focused on zkSync awareness, more than 100 projects are currently running on zkSync, demonstrating rapid ecosystem growth. Below are some of the key DApps operating within zkSync:
- Curve: One of the earliest and most influential automated market maker (AMM) exchanges. Although Curve’s total value locked (TVL) on zkSync is smaller than on other networks, growing adoption signals positive momentum.
- ZigZag: A noncustodial order-book DEX powered by zk-Rollups, enabling gas-free spot trading directly from user wallets. ZigZag also provides a bridge connecting zkSync and Ethereum.
- Yearn Finance: A yield-optimizing protocol offering automated investment strategies. Originally built on Ethereum, it now integrates with zkSync via Argent wallet support.
- Taker Protocol: A DAO-based liquidity framework that supports crypto lending, borrowing, NFT renting, and synthetic assets, expanding zkSync’s DeFi utility.
- Mute.io: A DAO-governed AMM, IDO, and farming protocol built entirely on zk-Rollups. It provides ultra-fast, gas-free transactions while enhancing user privacy through zk technology.
Conclusion
Zk-Rollups have revolutionized Ethereum’s scalability and efficiency. The evolution from zkSync 1.0 to 2.0 demonstrates ongoing improvement and innovation. As Ethereum continues to hold long-term significance in the blockchain ecosystem, zkSync’s zero-knowledge proof systems may well become a key driver of its decentralized future.
Since its inception in 2019, zkSync has consistently proven its value by enabling cheaper, faster, and more secure transactions. With numerous DApps adopting zkSync and more upgrades on the horizon, zk-Rollups have exceeded early expectations. Over time, Ethereum will likely act as the foundational data availability layer supporting zkSync and similar L2 technologies. Find this article useful? Read more in our Blog.
FAQs
What is the main purpose of zkSync?
ZkSync enhances Ethereum’s scalability and reduces gas fees by processing transactions off-chain while preserving on-chain security.
How does zkSync differ from Optimistic Rollups?
Optimistic Rollups assume transactions are valid until challenged, while zkSync instantly verifies validity using cryptographic proofs.
What makes zkSync cheaper than Ethereum?
ZkSync batches multiple transactions into a single rollup, significantly reducing gas costs while maintaining the same security level.
How many transactions per second can zkSync process?
ZkSync 1.0 supports around 3,000 TPS, while zk-Porter could raise that number to 20,000 TPS.
Is zkSync EVM-compatible?
zkSync 2.0 introduces zkEVM functionality, enabling native execution of Ethereum smart contracts with zero-knowledge proofs.
